
An ounce of information

Article by Pnut King
Published on 07/26/2023 in Peanut Science
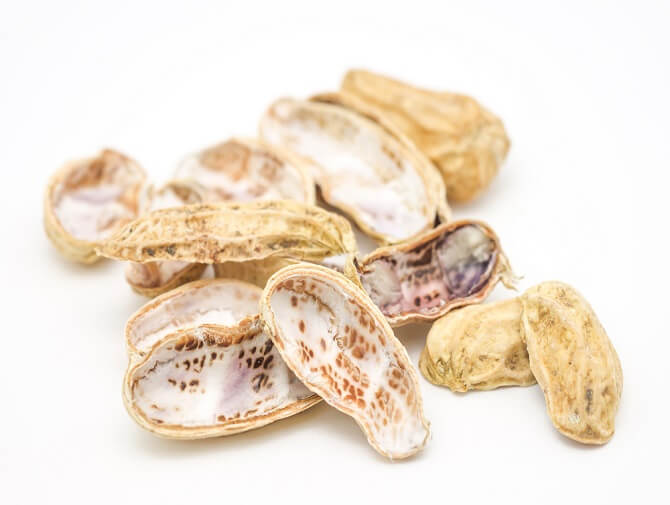
Have you ever gazed at the pile of peanut shells left over from your hearty snack and wondered what to do with them?
Well, let us tell you.
When it comes to the peanut plant, we often focus on the nutritious groundnuts that we love so much. But today, let’s talk about a part of the peanut that doesn't always get the spotlight but deserves some serious praise – the humble peanut and its shell.
Peanut shells are an abundant byproduct of our love for peanuts. As we enjoy the delicious peanuts, around 21-29% of the dried peanut pod’s weight is left as groundnut shell residuals.
Approximately 11 million metric tons of groundnut shell waste is generated each year from the groundnut industry, and with China contributing roughly 40% of global groundnuts, they account for the majority of this wastage. But in India, the volume of peanut waste also amounts to a significant number, considering the sheer volume of peanut production – a sizable 21%. But these shells are not mere waste; they’re a treasure trove of potential.
Here's a fun fact: Peanut shells hold a wealth of value. They are rich in carbon, cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin – components that make them far mightier than they might seem at first glance.
These organic compounds make peanut shells an incredible addition to a compost heap. The carbon in the shells acts as a potent energy source for the microorganisms that break down compost, and as the shells decompose slowly, they release their nutrients gradually – contributing to the richness of the compost.
But the benefits of these shells aren’t limited to gardens. Did you know that peanut shells can also contribute to renewable energy? That’s right, they also have vast industrial potential.
In a world where sustainability is no longer just a “nice-to-have” but a necessity, every bit of resource efficiency matters. Peanut shells can be converted into various bioproducts such as biodiesel and bioethanol, contributing to the generation of renewable energy. In fact, peanut shells have a high calorific value and can generate 1.25 megawatt-hours (MWh) of electricity per ton – that’s enough to power the average home in the US for over 1.2 months!
They can also be used on farms for animal feedstock. Small fractions of these shells can be integrated into animal feed, especially for cattle, offering an additional way to utilise this abundant resource.
This contribution to sustainable energy solutions and feedstock, along with their potential uses in enzyme production, dyes, and heavy metal degradation, positions peanut shells as a promising bio-resource.
Now, imagine the environmental impact we can make if we started considering these peanut shells not as a waste product but as an opportunity.
Instead of just throwing them away, we can recognise the potential of the humble peanut inshell casings and transform them into something valuable – compost for our gardens, feed for our animals, and even renewable energy for our homes.
Peanut shells – they're more than just casings. They're a testament to the power of nature, the value of sustainability, and the potential that lies in every bit of the peanut plant.
With over 17 years of experience in the peanut industry and numerous awards recognising his contributions, he founded Agrocrops in 2008, a leading global peanut company. His passion for peanuts drives his commitment to improving the industry for all stakeholders and promoting sustainability.

Published on 05/10/2023
Published on 05/04/2023

Published on 04/10/2023

Published on 04/05/2023