
What defines a good market in the peanut industry? Does a market with in-depth consumption prospects with high volatility make a good market?

Global Peanut Market
Winter in Gujarat has progressed about halfway, impacting exports,

Peanut Innovation
Peanut-derived surfactants represent a pioneering advancement in the field

Sustainability
Pre-harvest sprouting in peanuts refers to the germination of seeds

Good Agri Practices
Organic manure can play a crucial role in groundnut cultivation by
MARKET WIZARD
Demand
If substantial demand exists, can we classify the market as favourable? Consider markets in Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand, where demand persists throughout the year, and prices fluctuate with each transaction. Despite a collective import volume of 400k tons annually, daily volatility, and gross margins ranging from 3-5%, can this be deemed a robust market? If high volume coupled with high volatility is undesirable, how about a market like China, with 3 million tons of imports, low volatility, and 3-5% margins? Well, we all know the answer to it, don't we? Therefore, consistent demand alone does not guarantee a good market. What, then, defines a good market?
Supply
Does a good market definition hinge on a surplus or scarcity of supply? Consider China's production of 18 million tons and India's 9 million tons, where, on average, 80% of their production is consumed domestically. In these nations, the intricate interplay between harvest and consumption results in a continual and steady rise in peanut prices. Despite high production, new product launches, processors, and shippers emerge yearly. If supply constraints persist, these regions with abundant supply resort to imports to meet demand. Consequently, the impact on consumption is marginal, and the primary effect lies in price fluctuations, whether the supply is ample or limited.
In summary, determining the quality of a market within the peanut industry is inherently tied to a significant "X" factor called "sentiment." Although concrete supply and demand statistics are vital, the market's perception carries considerable weight. Simply put, a 10,000-ton stock may be considered inadequate in a good market scenario, while in an unfavourable one, 100 tons could be deemed excessive. Ain't that true?
Godspeed peanuts.

The Fascinating History of Peanuts and Coke
This fascinating culinary tradition that involves pairing peanuts and Coke? It's not a recent discovery it dates back to the early 20th century and has its roots in the Southern region. The surprising thing is, it all started because peanuts and Coke were both accessible and affordable. What's truly intriguing is the perfect blend of flavors - the sweetness of Coke and the savory crunch of peanuts come together to create a uniquely American taste sensation. It's one of those unknown facts that highlight how regional quirks can turn into beloved traditions, embraced by both locals and adventurous taste explorers alike.
Global Peanut Market
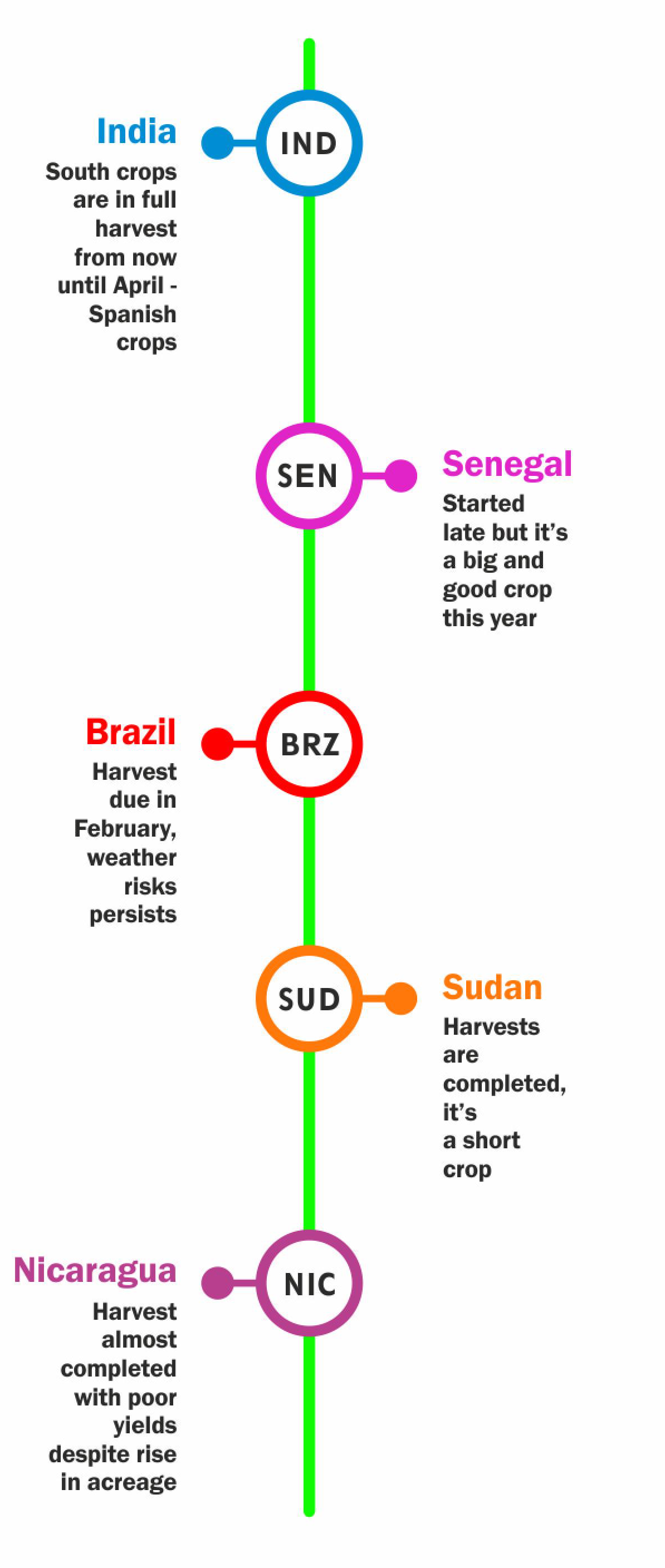
The winter 2023 crop in Gujarat is currently at 30%, with certain regions holding 10%-50% of stocks. This disparity has led to farmers' reluctance to sell, impacting the demand for Rabi 2024 sowing, which is currently poor. Fennel and Psyllium Husk in Gujarat have tripled, causing a decline in groundnut acreage for the Rabi crop. Local demand for oil and snacks in January is also low.
RAJASTHAN:In Rajasthan, crop quality and yields were poor, preventing exports, but domestic demand was good.
About 40-50% of peanut stocks remain with farmers and stockists. Despite the government purchasing at the MSP rate @ 63, it is deemed unsatisfactory for farmers, and domestic support is limited in January.
Karnataka arrivals started in many market yards in the southern region, with low arrivals, except in Raichur, Yadgir, and Gajendragadh. Sowing in Karnataka is at 30% only. Telangana is experiencing peak arrivals, slowing down the prices. Export demand is present and expected to continue until Apri. Tamil Nadu's summer crop is expected to arrive by the end of February, with a 10% higher yield than the previous year. Orissa's new crop is anticipated in mid-February; sowing in Orissa was reported at 80% of last year's levels.


The final USDA Crop Production Report discloses a slightly lower tonnage of 2,945,010 fst for the 2023 crop, with persistent quality issues, notably aflatoxin. Market activity concentrated on mediums and jumbos, maintaining prices at 67, 68, and 69/70 for runner splits, mediums, and jumbos respectively. Runner jumbos are tightening, potentially leading to a rise due to lower yields and demand, while spec material commands a premium. First-quarter availability, especially for blanched wholes, is tight, and buyers hope for price reductions with potential 2024 crop increases. Aflatoxin persists, impacting blanched and 32/42 varieties, with limited blanching space until May 2024. Raw peanuts prices range between 1800 and 1900 USD CIF EU. Amid global supply uncertainties, potential issues in Argentina, and escalating quality concerns in the US, challenges in the peanut market are anticipated. .
The current harvest reflects 2023's favourable conditions. Still, it faces challenges ahead, notably a looming 15-20 day period of high temperatures in February, critical for crop yields, especially in phenological states R3-R4 short cycles and long cycles R2-R3. Concerns mount over potential crop stress due to insufficient soil moisture. Despite a calm post-year-end market, there's anticipation of a good harvest and possible price reductions. However, worries persist about impending shortages in Argentina's last months of loads to Europe (March/April/May 2024), impacting shipment volumes. Climate uncertainties heighten the risks, emphasizing the need for timely rain to ensure crop volume and quality. Market participants brace for potential supply and pricing fluctuations, closely monitoring developments in Argentina's harvest and their global market ramifications.


The 2024 crop faces challenges as insufficient rain and high temperatures in November and December have impacted early yields. While January rains benefited crop health, concerns about potential heavy rains during the main harvest period, similar to the challenges in the 2023 crop, have arisen. Despite uncertainties, overall weather conditions suggest a below-average crop outcome, yet to be confirmed. Initial indications point to a 10-15% increase in planting compared to the last season. Still, Brazil is expected to harvest a similar volume due to the lack of rain since October plantings. A more accurate assessment of yields and quality is anticipated within a month, with harvesting scheduled to commence in late February.
One of the weakest trends witnessed in China this January 2024, despite the new year just around the corner. The oil prices were seen trading between 1700$-1800$ with stringent QCs, and oil-crushing factories kept lowering their procurement prices daily. Local exporters faced poor margins and poor export volumes. The prices remained stagnant, and interest in importing Sudan, Senegal and other origins was seen at pessimistic levels. Futures trended between 8700-8900 RMB. Blanched prices were stagnant at 1300$ FOB 6171. Post-CNY, the market could be even worse.


Sudan
Sudan faces problems with peanut sales due to Red Sea issues. Sudan peanuts have a retail price range of $2.40 to $6.23 per kilogram or $1.09 to $2.83 per pound. For January shipments, prices are around $1150 CIF Qingdao.
Senegal
The market is slow compared to the 2023 season amid higher prices and a lack of Chinese buyers. The MSP at 285 CFA per ton is extraordinary at the moment. The ex-factory prices of oil-crushing grades with splits range from $875 to $950 per ton, while the 55 grade costs $1155 ex-factory
Gambia
The government has set a price of 280 CFA per ton for farmer procurement. The retail price range in Gambian dalasi for groundnuts is between $0.65 and $2.16 per kg.

Editor’s Pick

Breakthrough Victoria shells out $12 million for peanut allergy treatment developer Aravax
Breakthrough Victoria, a government-funded initiative, has invested $12 million in Aravax, contributing to a $66 million funding round for the biotechnology company. Aravax is focused on developing a groundbreaking peanut allergy treatment, specifically its immunotherapy product, PVX108, which utilizes synthetic peptides to mimic crucial parts of peanut proteins, retraining the immune system. Unlike current treatments requiring daily doses, Aravax's solution is administered monthly, based on early research conducted at Alfred Health and Monash University. Grant Dooley, CEO of Breakthrough Victoria, expressed excitement about the investment, highlighting the potential global impact of this therapy developed in Victoria. Aravax has gained approval from the U.S. FDA and Australia's TGA for Phase 2 trials, building on the success of Phase 1 trials conducted with adults in 2018. The upcoming Phase 2 trials will involve children aged 4 to 17.

Mr.Jeffy Xu
Shanghai carry trade co ltd
Say about you
I am a Vice General Manager with a background in agricultural technology research within state-owned enterprises. Currently,involved in international trade of agricultural products at a trading company.
Do you think AI (artificial intelligence) will take over the growing of the ground?
The application of AI in the field of agriculture is constantly developing and expanding, but it may provide a lot of assistance in the future of the cultivation of the ground, but the ability to take over the entire cultivation process is very small.
Cultivar Highlights

Unveiling the Tallest and Shortest Peanut Cultivars Achieved Through Modified Plant Density.
Peanuts are a significant global oilseed crop, with seed yield depending on various management practices, especially those related to plant spacing, both between and within plants. Determining the optimum plant population density is crucial for achieving optimal yield.In an experiment conducted in Iraq, a randomized complete block design was used, with three main plots representing different plant densities and 17 subplots representing various plant cultivars and genotypes, each with three replications. The plant densities tested were 57,142, 71,429, and 95,238 plants/ha, arranged in a rectangular pattern.
...main plots representing different plant densities and 17 subplots representing...
Higher plant density resulted in significantly greater plant height compared to lower densities. The IND-IS-10 genotype cultivated at the highest plant density exhibited the tallest plants, reaching a height of 70.3 cm, while the GNIS-5 genotype at a moderate plant density displayed the shortest plants, measuring 41.8 cm. Whereas the average peanut plant height ranged from 44 to 53 cm, falling within the normal category. These results indicate the influence of both genetic diversity and other environmental factors related to plant distribution.
Reference: Dheya P Y, Ahmad Hussain, Effect of genotype and plant density on growth characteristics and yield of Peanut (Archis hypogaea) in Iraq Effect of Genotype and Plant Density on Growth Characteristics, and Yield of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) in Central Region of Iraq. Agri Res&Tech: Open Access J. 2019; 19(3): 556092.
Peanut Innovation

Peanut-Based Surfactants in Textile Processing
Peanut-derived surfactants represent a pioneering advancement in the field of surface-active agents. Surfactants, compounds capable of reducing surface tension between two phases, typically liquids and solids or liquids and gases, play a crucial role in various industrial processes. Peanut-derived surfactants, derived from compounds found in peanuts like fatty acids and proteins, effectively reduce interfacial tension between different phases. This enhances emulsion stability and facilitates the dispersion of substances that would otherwise be immiscible. In the textile industry, peanut-based surfactants effectively remove impurities and prepare fabrics for dyeing. Their gentle nature prevents damage to delicate fibers, rendering them suitable for high-quality textiles. The innovation lies in sustainably sourcing these surfactants from peanuts, offering a biodegradable and environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic surfactants derived from petrochemicals. This ensures efficient textile processing and aligns with the industry's increasing demand for eco-friendly solutions.
Current Crops
Peanut Sustainability

Sustainable Practices for Peanut Pre-harvest Sprouting
Pre-harvest sprouting in peanuts refers to the germination of seeds while still on the plant before the crop is harvested. This can be a concern for farmers as it negatively impacts the quality of the peanuts. Implementing sustainable practices in peanut cultivation can help mitigate pre-harvest sprouting while minimizing environmental impact. Here are some sustainable approaches i.e., Crop Rotation in peanut crops with other crops to break the cycle of diseases and pests. This helps maintain soil health and reduces the risk of pre-harvest sprouting. Planting cover crops during the off-season can help protect and improve soil structure. Cover crops prevent soil erosion, enhance water retention, and promote overall soil health. Adopting conservation tillage practices to minimize soil disturbance. Reduced tillage helps maintain soil structure, increases water retention, and decreases the risk of pre-harvest sprouting. Varietal Selection of peanut varieties that are less prone to pre- harvest sprouting. Some varieties have been developed to
...resist sprouting, and selecting these can contribute to a more sustainable peanut production system...
Timing of harvesting peanuts at the appropriate maturity stage to minimize the risk of pre-harvest sprouting. Timely harvesting, when peanuts are fully mature, can help reduce the chances of germination on the plant. Proper water management is crucial. Avoid over-irrigation, as excessive moisture can contribute to pre- harvest sprouting. Implement efficient irrigation practices to maintain optimal soil moisture levels. Implementation of Integrated Pest Management strategies to control pests and diseases. Biological control methods and the judicious use of pesticides, when necessary, can help maintain a balanced ecosystem. Educate farmers about sustainable peanut farming practices, including the importance of proper crop management, soil health, and the impact of pre-harvest sprouting. Providing training programs can help farmers adopt more sustainable approaches. Regular monitor peanut fields for signs of pre-harvest sprouting and other issues. Support research initiatives focused on sustainable peanut farming practices, including disease-resistant varieties and environmentally friendly pest control methods. Encourage community engagement and collaboration among farmers to share knowledge and experiences regarding sustainable peanut farming. This can foster a supportive network that promotes best practices. By integrating these sustainable practices, peanut farmers can minimize the risk of pre-harvest sprouting while promoting environmental stewardship and long-term viability in peanut cultivation.
Good Agricultural Practices

Optimal Groundnut Farming with Organic Manure
Organic manure can play a crucial role in groundnut cultivation by providing essential nutrients to the soil naturally and sustainably. Organic manure is rich in essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients. These nutrients enhance soil fertility and promote healthy plant growth, contributing to increased yields. Organic manure helps improve soil structure. It enhances the soil's water retention capacity, drainage, and aeration, creating a favourable environment for groundnut root development where nutrients slowly over time, providing a sustained supply of nutrients to the groundnut plants. This contrasts with synthetic fertilizers, which may release nutrients rapidly and lead to nutrient imbalances. It supports beneficial microbial activity in the soil. These microorganisms help break down organic material, release nutrients, and contribute to the overall health of the soil ecosystem. Reduced Environmental Impact Organic manure are derived from natural sources, reducing the environmental impact associated with the production and use of synthetic fertilizers. Weed Suppression Applying organic mulch or manure around groundnut plants can help suppress weeds. This reduces competition for nutrients and water, promoting better groundnut growth. Some organic amendments, such as compost, have been shown to suppress certain soil-borne diseases. The organic matter in manure improves the water-holding capacity of the soil. This is particularly beneficial during dry periods, as it helps groundnut plants access water more efficiently. Reduced Soil Erosion By improving soil structure and promoting the growth of ground cover, organic matter helps reduce soil erosion. Farmers can often produce their organic amendments or source them locally, reducing input costs. Proper management practices, including composting and application timing, can optimize the benefits of organic amendments in sustainable groundnut farming.
